IT BAND SYNDROME; FROM INFLAMMATION TO RESTORATION WITH AYURVEDA!
IT Band Syndrome(Iliotibial Band Syndrome/ITBS) is an overuse injury characterized by pain on the outer(later)side of the knee, caused by inflammation or irritation of the iliotibial band(IT band) as it rubs against the lateral femoral epicondyle(bony prominence on the outer part of (femur/thigh bone)during repetitive knee movements.
The iliotibial band runs from the hip (iliac crest) to the lateral portion of the shinbone (tibia), just below the knee. It is a thick band of fascia (connective tissue) that runs along the outside of the thigh. It is formed when the fibers of two muscles unite.
- Tensor fasciae latae(TFL).
- Gluteus maximus.
The IT band plays a major role in stabilizing the knee and hip during activities like walking, running, cycling, and climbing etc.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF IT BAND SYNDROME(ITBS):
During repetitive activities; especially running or cycling-the knee continuously flexes and extends. As this happens:
- The IT band glides over the lateral femoral epicondyle.
- Repetitive friction between the band and bone leads to inflammation, thickening, or tightness of the IT band.
- This causes pain and tenderness on the outer side of the knee, especially during the activity.
CLINICAL FEATURES OF IT BAND SYNDROME(ITBS):
1.Lateral Knee Pain(Most Characteristic Feature):
- Site: Pain is localized at the lateral femoral condyle(outer side of the knee).
- Nature of pain: Sharp or burning pain during activity, especially running, climbing stairs, or cycling.
- Worsens with: Downhill running, prolonged sitting with knee bent, or after activity.
- Relieved by: Rest and stopping the activity.
2. Pain that increases with Activity:
- Running downhill.
- Climbing stairs.
- Cycling.
- Squatting.
- Walking or running on uneven surfaces.
Pain often subsides with rest, but returns once activity resumes.
3. Pain with pressure:
- Pain may worsen when pressing on the lateral side of the knee or lying on the affected side.
4.Tenderness:
- On palpation over the lateral epicondyle.
- Sometimes, a snapping sensation may be felt when the IT band rubs over the condyle during knee flexion and extension.
5. Swelling or Thickening:
- Localized swelling over the lateral knee may be seen in more inflamed cases.
- It is not always visible but they feel like a thickened band on palpation.
6.Tightness:
- The IT band and tensor fascia lata(TFL) may feel tightened and shortened.
7.Gait Changes:
- In chronic cases, patients may alter their gait to reduce pain.
- It can lead to secondary issues in the hip or ankle due to compensatory mechanisms.
8. Snapping or Popping sensation:
- Snapping or popping sound or feeling as the knee bends and straightens, due to IT band rubbing over the bone.
CLINICAL TESTS FOR IT BAND SYNDROME(ITBS):
There are several physical examination tests used to assess ITBS.
1. Ober’s Test:
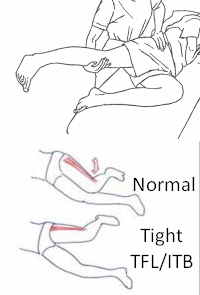
- Purpose: To assess the tightness of the iliotibial band.
Procedure:
- The patient lies on their unaffected side.
- The examiner stands behind the patient and stabilizes the pelvis.
- The affected leg is flexed at the knee at 90 degrees and then abducted and extended at the hip.
- The leg is then allowed to drop toward the table passively.
Positive sign:
- The leg remains in an abducted position and does not fall to the table, indicating a tight IT band.
2. Noble’s Compression Test:
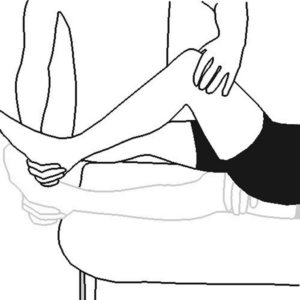
- Purpose: To reproduce pain associated with ITBS and confirm inflammation over the lateral femoral epicondyle.
Procedure:
- The patient lies supine with the hip and knee flexed at 90 degrees.
- The examiner applies pressure to the lateral femoral epicondyle(about 1-2 cm above the lateral joint line).
- The knee is then slowly extended while maintaining pressure.
Positive sign:
- Pain over the lateral femoral epicondyle around 30 degrees of flexion during knee extension suggests ITBS.
3. Renne’s Test:
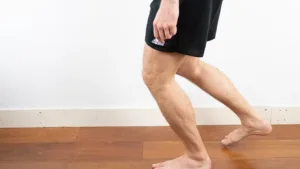
- Purpose: A variation of Noble’s test, used to detect lateral knee pain from ITBS in weight bearing.
Procedure:
- The patient stands and the examiner applies pressure to the lateral femoral epicondyle.
- The patient then performs a single-leg squat or knee flexion to about 30-40 degrees.
Positive sign:
- Pain or discomfort at the lateral knee, especially around 30 degrees, indicates ITBS.
4. Modified Thomas Test:
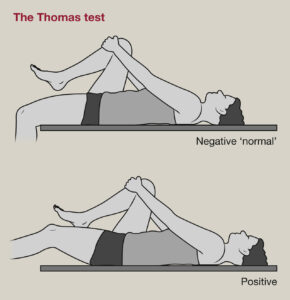
- Purpose: To assess tightness in the band iliopsoas, rectus femoris, and IT band.
Procedure:
- The patient lies supine and pulls one knee to their chest.
- The examiner observes the opposite leg for lifting off the table, abduction, or external rotation.
Positive signs for ITBS:
- The opposite leg abducts or externally rotates, suggesting tightness of the IT band.
5. Palpation and Functional Tests:
- Palpation: Tenderness upon palpation over the lateral femoral epicondyle or along the IT band.
Functional Tests:
- Pain is often reproduced with activities such as downhill running, squatting, or going downstairs.
Additional Diagnostic Tools:
a)MRI(Magnetic Resonance Imaging):
- Thickened IT band.
- Inflammation or fluid between the It band and lateral femoral epicondyle.
- It helps to rule out lateral meniscus tears or joint pathology.
b)X-Ray:
- Usually Normal.
- Done to rule out bony abnormalities.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF IT BAND SYNDROME(ITBS):
1. Lateral Meniscus Tear:
Pain Location:
- Lateral Joint line(deeper than ITBS).
Key Symptoms:
- Locking or catching of the knee.
- Pain worsens with twisting or squatting.
- History of trauma or sudden twisting injury.
Clinical Tests:
- McMurray’s test.
- Thessaly test.
Imaging:
- MRI confirms the diagnosis.
2.Lateral Collateral Ligament(LCL)Injury:
Pain:
- Over collateral ligament(slightly above or below the lateral joint line).
Key Symptoms:
- History of varus(inward)stress or trauma to the medial knee.
- Instability during side-to-side movements.
- Localized swelling and tenderness.
Clinical Tests:
- Varus stress positive.
Imaging:
- MRI is useful to assess ligament integrity.
3. Popliteus Tendinopathy or Injury:
Pain:
- The posterolateral aspect of the knee(deeper than ITB).
Key Symptoms:
- Pain during downhill running or declaration.
- Snapping or catching sensation.
Clinical Tests:
- Restricted knee flexion.
- External tibial rotation causes pain.
Imaging:
- MRI shows inflammation or tears.
4. Biceps Femoris Tendinopathy:
Pain:
- Posterolateral knee, near fibula head.
Key Symptoms:
- Pain with resisted knee flexion.
- Local tenderness at the fibular head.
- Common in sprinting athletes.
Clinical Clues:
- Tender insertion at the fibular head differentiates from ITBS.
Imaging:
- Ultrasound or MRI may show tendon changes.
5.Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome(PFPS):
- Pain Location: Anterior or peripatellar, which can refer to the lateral side.
Key Symptoms:
- Pain worsens with prolonged sitting, stair climbing, or squatting.
- No specific point tenderness over ITB.
Clinical Tests:
- Clarke’s Test(positive).
Imaging:
- An X-ray may show patellar maltracking.
6. Stress Fracture of Lateral Tibial Plateau or Femur:
- Pain: Lateral proximal tibia or distal femur.
Key Symptoms:
- Deep, aching pain worsens with weight bearing.
- It may occur in endurance athletes or due to overtraining.
Clinical Clues:
- Pain is constant, not activity-specific like ITBS.
Imaging:
- Bone scan or MRI essential(X-ray may be normal initially).
7. Superior Tibiofibular Joint Dysfunction:
Pain:
- The lateral side of the knee, near the fibula head.
Key Symptoms:
- Pain with rotational knee movement.
- Clicking or locking sensation.
Clinical Clues:
- Palpation over the fibular head reproduces pain.
Imaging:
- MRI or joint-specific imaging helps.
8. Referred Pain from Hip or Lumbar Spine:
- Pain: Variable; may present laterally.
Key Symptoms:
- Associated with low back pain or hip stiffness.
- Neurological symptoms like numbness or tingling.
Clinical Tests:
- Straight leg raise.
- FABER test.
Imaging:
- Lumbar spine MRI or hip X-ray.
TREATMENT OF IT BAND SYNDROME IN MAURYA AYURVEDA
In order to promote holistic well-being and optimal health, our hospital provides complete treatments by skilfully combining Ayurveda,physiotherapy and acupuncture.
ROLE OF AYURVEDA IN IT BAND SYNDROME(ITBS):
1. PODI KIZHI:

In this ayurvedic treatment, heated herbal powders wrapped in a cotton pouch known as a Kizhi ,which is warmed and massage is done to the body. Podi Kizhi is frequently made at our hospital using KOLAKULATHADI CHOORNAM. It usually takes 40 to 45 minutes to complete.
Advantages of PODI KIZHI in ITBS:
- Reduces muscles and tightness.
- Improves blood circulation.
- Reduces pain and inflammation.
- It enhances mobility.
- It speeds up recovery.
- It prepares the body for better rehab.
2. NADI SWEDAM:
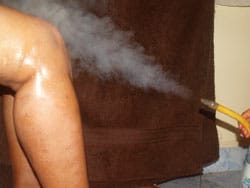
A hose or tube is used to perform Nadi Swedam, a form of localized steam therapy. Usually, DASHAMOOLA KASHAYAM is used to produce steam. Typically, the steaming procedure takes ten to fifteen minutes.
The advantages of NADI SWEDA in ITBS:
- It aids in the relaxation of tissues and muscles.
- It helps with circulation.
- It makes muscles less rigid.
- It helps to lessen discomfort/pain.
- It reduces muscle tension.
3. DHARA:
The therapeutic procedure known as dhara involves applying a warm steady stream of medicinal liquids, such as buttermilk, milk, herbal oils, or decoctions, to the affected area.
Dhara is classified based on the application area and the liquid used.
We usually perform kashaya dhara and Dhanyamla dhara in these situations.
- In KASHAYA DHARA, herbal mixtures are used topically. Dashamoola Kashayam is used for this dhara.
- DHANYAMLA DHARA: In this kind of specialist treatment, a continuous stream of Dhanyamla, a fermented medicinal liquid, is applied to the body.
Advantages of DHARA
- It helps to lessen inflammation.
- It eases pain .
- Reduces muscle tension and spasm.
- Improves circulation.
- It enhances effect of physiotherapy.
4. LEPAM:
In Ayurveda, the term “lepam” refers to the application of a medicinal herbal paste to the area of pain and swelling. That is left unattended for around 30 to 60 minutes. Once the paste has dried, it may usually be washed off. Usually, we use RASNADI and GRAHADHOOMADI in Jambeera (lemon juice) to apply lepam.
Advantages of LEPAM
- It aids in lowering inflammation and swelling.
- Aids in easing stiffness and discomfort in the muscles.
- Lessens pain as well.
ROLE OF PHYSIOTHERAPY IN IT BAND SYNDROME(ITBS):
1. Pain and Inflammation management:
Modalities:
- Cryotherapy(ice packets)To reduce inflammation in the acute phase.

- Ultrasound Therapy: Promotes tissue healing and reduces pain.

- TENS(Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation): For pain relief.

2. Stretching Techniques:
It focuses on reducing the tightness of the IT band and associated structures.
- IT band stretch: Standing cross-legged side bend or wall stretch.
- Tensor Fasciae Latae stretch.
- Gluteal Stretch(esp:gluteus maximus and medius).
- Hamstring and Quadriceps stretching: To balance muscle length.
Hold Stretches for 30 seconds, repeat 2-3 times per side, daily.
3. Myofascial Release:
- Foam rolling on the lateral thigh(IT band region)to reduce fascia tightness.
- Manual Release Techniques: Performed by physiotherapists to address the trigger points.
- Instrument-Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization: Like the Gastron technique, to break adhesions and improve fascia mobility.
4. Strengthening Exercises:
Mainly targeting weak hip and core muscles, which often causes compensation and stress on the IT band.
Key muscles to strengthen:
- Gluteus maximus and medius.
- Hip abductors and external rotators.
- Core muscles(especially obliques and transversus abdominis).
Examples: Side lying leg lifts.
- Clamshells with resistance bands.
- Bridges with hip abduction.
- Step-ups and single-leg squats.
- Monster walks with resistance bands.
Strats with low resistance and gradually progress.
5. Neuromuscular Re-education:
It helps correct faulty movement patterns, contributing to ITBS.
- Gait analysis and correction.
- Running retraining(shorter strides, cadence adjustment).
- Balance training(single leg balance, BOSU ball exercises).
6. Taping and Bracing:
- Kinesiology Taping: Reduces strain on the IT band, و supports weak muscles.
- Lateral knee support braces(used short term during painful phases).
7. Postural Correction:
- Assessment of pelvic tilt, leg length discrepancies, and foot biomechanics(flat foot, overpronation).
- Custom orthotics or arch support if foot issues are identified.
- Education on proper footwear.
ROLE OF ACUPUNCTURE IN IT BAND SYNDROME(ITBS):
العلاج بالإبر plays a significant therapeutic role in ITBS, offering both symptom relief and functional improvement.
Techniques used in Acupuncture for IT Band Syndrome:
1.Local Needling:
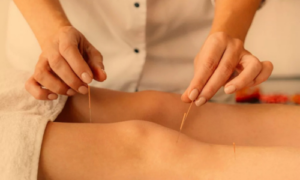
Target areas:
- Lateral thigh(along IT band).
- Lateral epicondyle of femur(site of friction and inflammation).
- Tensor fascia latae(TFL).
- Gluteus maximus.
Effect:
- Reduces local muscle tension
- Stimulates blood flow.
- Relieves pain.
2.Trigger Point Acupuncture(Dry needling):
Often used for tightness and myofascial trigger points in:
- TFL
- Gluteus medius and minimus.
- Vastus lateralis.
Effect:
- Deactivates trigger points.
- Improves flexibility of surrounding structures.
3.Distal Point Needling(Channel Theory based):
Common distal points:
- GB34(Yanglingquan): Influential point for tendons.
- GB31(Fengshi): On the lateral thigh, along the IT band.
- GB30(Huantiao): Deep point near the gluteus for hip imbalance.
- BL40(Weizhong): Supports lower limb tension release.
4. Electroacupuncture:
- A mild electrical current is applied to the needles.
- It is commonly used on tight muscles or tendon insertions.
- It enhances analgesic effects and improves circulation and healing.
5.Cupping:
Wet or Dry cupping can be applied over the IT band or gluteal area to:
- Release fascial restrictions.
- Improve lymphatic and blood circulation.
Key benefits of Acupuncture in IT Band Syndrome are:
- Pain reduction.
- Reduction of local inflammation.
- Release of myofascial tension.
- Improved blood flow and healing.
- Restoring muscle balance and function.
- Addressing contributing factors(Eg: hip/knee misalignment, gait issues).
DISCLAIMER: The information provided in this article is intended solely for educational purposes. Treatment decisions should be made exclusively by a well-qualified Ayurvedic physician. Self-medication is strongly discouraged.
Maurya Ayurveda Hospital,opposite to Sabine Hospital,Pezhakkapilly P.O,Muvattupuzha,Ernakulam;PIN:686673,Contact no:9947183000
Email: info@mauryaayurveda.com
مركز ماوريا أيورفيدا لتقويم العظام وإعادة التأهيل العصبي (مستشفى الأيورفيدا)