POLYCYSTIC OVARIAN SYNDROME(PCOS): FROM IMBALANCE TO INNER HARMONY THROUGH AYURVEDA
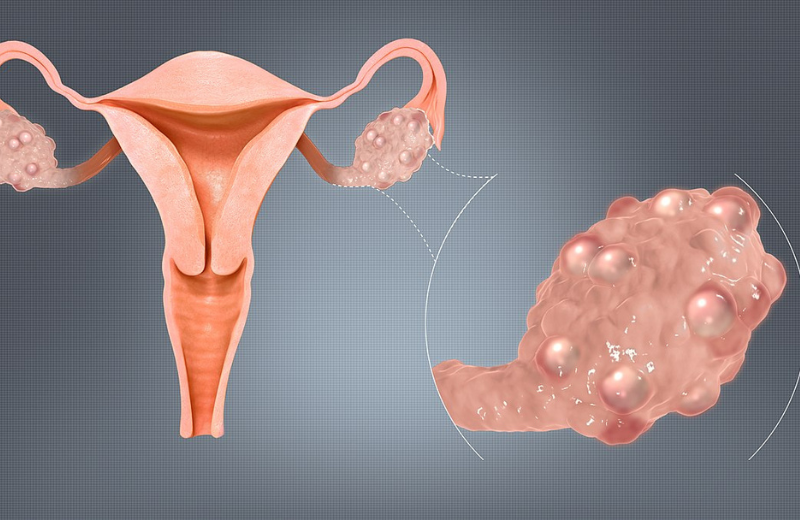
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome(PCOS) is a common hormonal imbalance disorder affecting women of reproductive age. It is a complex condition characterised by disturbances in metabolism, reproductive function, and hormone regulation.
Key Symptoms and Signs of PCOS
- Irregular or absent menstrual cycles.
- Multiple immature follicles(cysts) in the ovaries.
- Elevated androgen(male hormone) levels.
- Insulin resistance.
- Difficulty in conceiving.
- Weight gain, acne, excessive hair growth(hirsutism).
Ayurvedic view of PCOS
In Ayurveda, PCOS can be correlated with conditions such as:
-
Arthava Kshaya – Scanty or absent menstruation
-
Pushpagni Jatharini – A condition where the uterus suppresses menstruation and ovulation
-
Stree Vandhyatha – Female infertility
-
Granthi – Cyst-like formations in the Artavavaha Srotas (channels responsible for menstruation)
PCOS as a Tridoshic Disorder with Kapha Dominance
Ayurveda explains PCOS as a Tridoshic imbalance, with Kapha playing a dominant role and involvement of Vata and Pitta.
1. Kapha Dosha Involvement (Primary Factor)
-
Kapha governs structure, nourishment, and growth.
-
Excess Kapha leads to the thickening of tissues, the formation of cystic structures, and the blockage of Srotas.
-
It weakens Agni (digestive fire), slows down metabolism, and promotes Ama (toxins).
-
This results in weight gain, sluggish cycles, and hormonal imbalance.
2. Vata Dosha Involvement
-
Vata regulates movement, including ovulation, menstrual flow, and follicular development.
-
Vata imbalance leads to irregular cycles, painful periods, and obstruction in reproductive channels.
-
Contributes to mood swings, anxiety, and erratic hormonal activity.
3. Pitta Dosha Involvement
-
Pitta governs hormonal activity, metabolism, and transformation.
-
Pitta imbalance results in inflammation, acne, hair fall, and emotional irritability.
-
Influences insulin resistance and heat in reproductive tissues.
Samprapti (Ayurvedic Pathogenesis) of PCOS
-
-
Agnimandya (Low Digestive Fire) – Poor digestion weakens metabolism.
-
This leads to Ama Formation – Accumulation of toxins.
-
Vitiated Kapha obstructs the Artava Vaha Srotas (menstrual channels).
-
Blockage prevents proper follicle maturation and egg release (ovulation).
-
This results in:
-
Cyst formation
-
Irregular or absent menstruation
-
Hormonal imbalance
-
Challenges with fertility
-
-
Causes of PCOS
While the exact cause of PCOS is still not fully understood, research shows that PCOS develops due to a combination of hormonal, genetic, metabolic, and lifestyle factors.
1. Hormonal Imbalance
Hormonal imbalance is one of the primary contributors to PCOS.
Key Hormonal Changes
-
High androgen levels: Excess male hormones such as testosterone cause acne, facial/body hair growth, and scalp hair thinning.
-
Low progesterone: Due to irregular or absent ovulation, progesterone levels drop, causing irregular periods.
-
High LH levels: An elevated LH: FSH ratio can overstimulate the ovaries, increasing androgen production.
These hormonal disruptions interfere with normal menstrual cycles and ovulation.
2. Insulin Resistance
Many women with PCOS experience insulin resistance, meaning the body does not use insulin effectively.
Role of Insulin Resistance in PCOS
-
The pancreas produces more insulin to compensate.
-
High insulin levels stimulate the ovaries to make more androgens.
-
This leads to weight gain, irregular cycles, and worsening PCOS symptoms.
Insulin resistance can occur in both lean and overweight individuals, but it is more common in those with excess weight.
3. Genetic Predisposition
PCOS often runs in families, suggesting a genetic link.
Genetic Influence
-
Women with a mother or sister who has PCOS have a higher chance of developing it.
-
Several genes related to hormones, metabolism, and inflammation may play a role.
Although no single gene causes PCOS, genetics significantly contribute to risk.
4. Chronic Low-Grade Inflammation
PCOS is linked with chronic low-level inflammation.
Effects of Inflammation
-
Inflammation can trigger the ovaries to produce more androgens.
-
It is associated with obesity, poor diet, and metabolic imbalance.
This type of inflammation may play a role in the long-term health effects of PCOS.
5. Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Certain lifestyle habits and environmental exposures can worsen or trigger PCOS, especially in genetically predisposed women.
Major Lifestyle Influences
-
Poor diet: High intake of refined carbs, sugars, and processed foods worsens insulin resistance.
-
Lack of physical activity: Reduces insulin sensitivity and impacts metabolic health.
-
Stress and poor sleep: Disturb hormones and worsen symptoms.
-
Environmental toxins: May disrupt endocrine function.
6. Hypothalamic Pituitary Ovarian(HPO) Axis Dysfunction
The HPO axis controls menstrual cycles and hormone regulation.
HPO Axis Imbalance in PCOS
-
Abnormal signalling from the brain alters the production of LH and FSH.
-
This imbalance interferes with ovulation and egg development.
-
It contributes to irregular periods and hormonal imbalance.
7. Gut Microbiome Imbalance (Emerging Theory)
New studies show that the gut microbiome plays a role in metabolism, hormones, and inflammation.
Effects of Gut Imbalance
- Increases systemic inflammation
- Worsens insulin resistance
- Impacts hormone metabolism
Clinical Symptoms of PCOS
1. Menstrual Irregularities
Irregular periods are one of the most common symptoms of PCOS.
Types of Menstrual Irregularities
-
Oligomenorrhea: Infrequent menstrual cycles (typically fewer than 8 periods per year).
-
Amenorrhea: Complete absence of menstruation for 3 or more consecutive months.
-
Heavy or prolonged periods: When bleeding occurs, it may be heavier or last longer than normal due to the prolonged build-up of the endometrium.
Cause: These issues occur due to irregular or absent ovulation (anovulation), a hallmark of PCOS.
2. Hyperandrogenism (Excess Male Hormone Levels)
High androgen (male hormone) levels lead to several noticeable physical symptoms.
Common Signs of Hyperandrogenism
-
Hirsutism: Excess facial or body hair growth in areas such as the chin, chest, abdomen, back, or thighs.
-
Acne: Persistent or severe acne, especially on the jawline, chin, and back.
-
Alopecia: Thinning scalp hair (androgenic alopecia), often around the crown and temples.
-
Oily skin and seborrhea: Increased sebum production.
Cause: Ovaries produce excess androgens, including testosterone.
3. Polycystic Ovaries
Ultrasound findings may show enlarged ovaries containing multiple small follicles arranged in a “string of pearls” pattern.
Important Notes
-
Not all women with PCOS have cysts.
-
Having ovarian cysts alone does not mean a woman has PCOS.
-
Polycystic ovaries are more of a diagnostic feature than a symptom.
4. Infertility or Subfertility
One of the major reproductive concerns in PCOS is difficulty conceiving.
Reason: Irregular ovulation or lack of ovulation makes it harder to release eggs consistently.
PCOS is a leading cause of anovulatory infertility.
5. Weight Gain and Difficulty Losing Weight
Many women with PCOS experience:
-
Weight gain, particularly around the abdomen (central obesity).
-
Difficulty losing weight despite regular efforts.
Note:
Not all women with PCOS are overweight. Lean PCOS exists and may be underdiagnosed.
6. Insulin Resistance and Related Symptoms
Insulin resistance is extremely common in PCOS and increases the risk of several health issues.
Related Signs and Risks
-
Acanthosis nigricans: Dark, velvety skin patches on the neck, armpits, or groin.
-
Higher risk of type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
7. Mood Changes
Hormonal imbalances combined with physical symptoms can contribute to:
-
قلق
-
الاكتئاب
-
Mood swings
Infertility struggles and visible symptoms like acne or hirsutism may worsen emotional stress.
8. Fatigue and Poor Sleep
Women with PCOS often report:
-
Chronic fatigue
-
Low energy levels
-
Poor sleep quality
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) is also more common, especially in women with obesity.
9. Pelvic Pain
Some women experience:
-
Intermittent lower pelvic discomfort
-
Pain during periods or when ovarian cysts enlarge or rupture
Diagnosis of PCOS
Diagnosing Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) involves assessing clinical symptoms, physical examination findings, blood test results, and ultrasound imaging.
1. Clinical History (History Taking)
A detailed history is the first step in diagnosing PCOS. Doctors evaluate symptoms and hormonal patterns such as:
Menstrual History
-
Irregular periods
-
Absent periods (amenorrhea)
-
Very light or unusually heavy bleeding
Weight History
-
Unexplained weight gain
-
Difficulty losing weight
Skin Changes
-
Acne or oily skin
-
Dark, velvety skin patches (acanthosis nigricans) indicating insulin resistance
Hair Changes
-
Excess facial/body hair (hirsutism)
-
Scalp hair thinning
Fertility Issues
-
Difficulty conceiving
-
Recurrent miscarriages
Mood Changes
-
قلق
-
الاكتئاب
-
Mood swings
2. Physical Examination
A physical exam helps identify visible signs of hormonal imbalance and metabolic issues.
Key Assessments
-
BMI (Body Mass Index): To check for overweight or obesity
-
Waist circumference: Central obesity is common in PCOS
-
Signs of hyperandrogenism: Facial/body hair, acne, male-pattern baldness
-
Skin exam: Acanthosis nigricans suggests insulin resistance
3. Diagnostic Criteria (Rotterdam Criteria – 2003)
Most clinicians use the Rotterdam Criteria, which require any 2 out of 3 of the following:
a. Oligo- or Anovulation
-
Irregular or absent menstrual cycles
-
Cycles greater than 35 days
-
Fewer than 8 periods per year
b. Polycystic Ovaries on Ultrasound
-
12 or more follicles (2–9 mm) in at least one ovary
-
OR increased ovarian volume (>10 mL)
-
“String of pearls” appearance
c. Signs of Hyperandrogenism
(Clinical or biochemical)
-
Excess hair growth
-
Acne
-
Elevated testosterone or DHEAS on blood tests
Diagnosis can be made even if cysts are not visible on ultrasound.
4. Blood Investigations
Blood tests help confirm hormone imbalances and rule out other medical conditions.
a. Hormone Tests
-
LH & FSH: A ratio of 2:1 may suggest PCOS
-
Total and Free Testosterone: Often elevated
-
DHEAS: Another androgen that may be raised
-
Prolactin: To exclude prolactinoma
-
TSH: To rule out thyroid disorders
-
AMH (Anti-Müllerian Hormone): Often elevated due to increased follicle count
b. Glucose and Insulin Tests
-
Fasting blood glucose and fasting insulin
-
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): Gold standard to assess insulin resistance and diabetes risk
c. Lipid Profile
Since PCOS is associated with metabolic syndrome, testing includes:
-
Total cholesterol
-
LDL & HDL
-
Triglycerides
5. Pelvic Ultrasound (Transvaginal or Transabdominal)
Ultrasound is used to visualise the ovaries and assess structural features.
Common Findings
-
Multiple small follicles are arranged like a “string of pearls”
-
Enlarged ovaries
-
Increased ovarian stroma or volume
Treatment of PCOS at Maurya Ayurveda
At Maurya Ayurveda, our integrated approach offers a holistic and effective path to long-term PCOS management.
أيورفيدا Treatment for PCOS
Ayurvedic treatment offers a holistic approach, including internal medications, Panchakarma therapies, and external treatments, to balance hormones, improve metabolism, detoxify the body, and enhance reproductive health.
A. Internal Medications for PCOS
Common Ayurvedic formulations used in PCOS management include:
- Varanadi Kashayam
- Saptasaram Kashayam
- Amrthotharam Kashayam
- Shaddharanam Tab
- Abhayarishtam
- Hinguvachadi Gulika
- Kumaryasava
- Raja Pravartini Vati
- Kanasathahwadi Kashayam
- Pushyanuga Choornam
These medicines support digestion, reduce Ama (toxins), balance hormones, improve ovarian function, and regulate menstruation.
B. Panchakarma Treatment
Panchakarma therapies play a central role in removing toxins, reducing Kapha–Vata imbalance, and restoring normal ovarian function.
1. Snehapanam

Snehanam means Oleation, and Pana means oral intake. It refers to the oral administration of medicated ghee(Ghrita) or sometimes oil, in a gradually increasing dose over a few days, under the supervision of an Ayurvedic Physician.
Types of Snehapanam
- Shodhana Snehapanam – Preparatory for detoxification(panchakarma).
- Shamana Snehapanam – For pacification, it is used as a treatment without panchakarma.
Some commonly used ghee
- Phalasarpis: For gynaecological disorders, including fertility.
- Triphala Ghrita: Antioxidant and detoxifying.
- Sukumara Ghrita: For Vata predominant gynaecological issues.
- Ashwagandha Ghrita: For hormonal balance and nourishment.
Procedure of Snehapanam
- Initial assessment: To determine Agni(digestive fire), Prakriti(nature), and Dosha imbalance.
- Starting dose: Given on an empty stomach in the morning.
- Gradual increase: The dose increased daily depending on digestion and tolerance.
- Signs of proper oleation include:
✓ Soft skin
✓ Better appetite
✓ Lightness of body
✓ Smooth bowel movements.
Duration: 3–7 days, followed by a light diet
After Snehapanam, the treatment continues with either:
-
Panchakarma (Vamana or Virechana), or
-
Shamana Chikitsa (Pacifying treatments)
Benefits of Snehapanam in PCOS
-
Clears Ama (toxins)
-
Improves digestion & metabolism
-
Balances hormones
-
Supports ovulation
-
Nourishes tissues (Dhatu Poshana)
-
Aids weight loss
-
يقلل من الإجهاد
2. Vamanam (Emesis Therapy)

In the context of PCOS (Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome), where Kapha and Meda (fat tissue) play a significant role in the pathogenesis, Vamana is considered a highly effective Panchakarma therapy. When performed with the correct indications, preparation, and timing, Vamana helps eliminate excess Kapha and supports healthy ovarian function.
Indications of Vamana in PCOS
- Excessive weight gain.
- Heaviness in the body.
- Irregular periods with Kapha predominant symptoms(whitish discharge, sluggishness, lethargy).
- Kapha-dominant ovarian cysts
- Thick, oily skin with acne.
- Insulin resistance.
- Emotional dullness or mental fog.
موانع
Not suitable for:
- حمل
- Severe Vata conditions like dryness, weakness, anxiety, etc.
- Emaciated persons
- During menstruation
- Low haemoglobin or cardiac disorders
Procedure of Vamana
Vamana is carried out in three main phases:
1. Purva Karma (Pre-procedure)
a)Deepana and Pachana (3-5 days)
- Herbal medicines are given to enhance digestion and remove Ama (toxins).
- Examples: Trikatu, Panchakola Choornam, Hinguvashtaka Choornam.
b)Snehapana (Internal Oleation for 3–7 days)
Gradual intake of medicated ghee, such as:
-
Tiktaka Ghritam
-
Triphala Ghritam
Oleation continues until Samyak Snigdhata (proper signs of oleation) appear.
c)Abhyanga and swedana (2-3 days)
- Full body oil massage and steam therapy to liquefy Kapha and move it into the stomach for elimination.
2. Pradhana Karma (Main Procedure-Vamana)
-
Performed early morning between 6–8 AM on an empty stomach.
Process:
-
Patient is given Kapha-aggravating food or drink (milk, curd, sweet rice porridge)
-
Followed by Vamana drugs:
Madanaphala, Yashtimadhu Phanta, Vacha, Saindhava Lavana
The patient vomits several times until Samyak Vamana(proper emesis) signs appear:
-
Lightness of the body
-
Mental clarity
-
Reduction in Kapha symptoms
-
3. Pashchat Karma (Post procedure)
Includes:
-
Samsarjana Krama – gradual diet progression from Manda → Peya → Vilepi → normal diet
-
Adequate rest and light activity
-
Follow-up Ayurvedic medicines such as:
Triphala, Chandraprabha Vati, Raja Pravartini Vati
Benefits of Vamana in PCOS
-
-
Reduces excess Kapha
-
Helps regulate the menstrual cycle
-
Improves insulin sensitivity
-
Supports weight reduction
-
Reduces acne, oily skin, and pigmentation
-
Enhances energy and reduces mental fog
-
3. VIRECHANA (Purgation Therapy)
Virechana is one of the most effective Ayurvedic Panchakarma therapies for women with PCOS, especially when Kapha and Pitta imbalances are involved. It works by eliminating excess Doshas from the body—primarily through controlled purgation via the anal route—promoting hormonal balance and metabolic reset.
Five main stages of فيركانا
1. Purva Karma (Preparation)
-
Deepana and Pachana
-
Boosts digestive fire and reduces Ama (toxins)
-
Herbs used: Trikatu, Panchakola Choornam
-
-
Snehapana (Internal Oleation)
Intake of medicated ghee(eg, Tikta Ghrita or Triphala Ghrita) for 3-7 days to loosen deep-rooted toxins.
-
Abhyanga and Swedana
Oil massage and steam therapy help liquefy toxins and bring them into the GI tract for elimination.
2. Pradhana Karma (Main procedure)
- Administration of herbal purgatives such as Trivruth Lehya, Avipatti Choorna, or Eranda Taila.
-
Produces 10–15 bowel movements under supervision.
-
Purpose: Expel accumulated Doshas and metabolic waste.
3. Paschat Karma (Post-therapy care)
Samsarjana Krama (Post-Detox Diet)
-
Gradual diet progression from Manda → Peya → Vilepi → normal food
Lifestyle guidance
-
-
Rest and light activities
-
Avoid heavy physical or mental strain.
-
Benefits of Virechana in PCOS
-
Detoxifies the liver and blood
-
Enhances digestion and metabolism
-
Supports hormonal balance
-
Encourages regular ovulation
-
Reduces androgenic symptoms (acne, hair fall, hirsutism)
-
Promotes mental clarity and emotional stability
Contraindications of Virechana
-
حمل
-
Severe anemia
-
Extreme weakness or fatigue
-
Active infections
It must always be performed under the guidance of a qualified Ayurvedic physician.
4. Basti (Enema Therapy)
Basti/Vasti is an important Ayurvedic Panchakarma therapy in which medicated oils, herbal decoctions, or special formulations are administered through the rectum. It is primarily used to balance Vata Dosha, which plays a major role in PCOS due to hormonal disturbance, irregular cycles, ovarian dysfunction, and metabolic issues.
In Ayurveda, PCOS is considered a Kapha–Vata disorder, involving Rasa, Rakta, Meda, and Artava Dhatus, often due to Avarana (obstruction) of Vata by Kapha and Meda. Vasti helps remove this obstruction and restores normal Apana Vata functions related to menstruation and fertility.
Types of Vasti beneficial in PCOS
a. Niruha Vasti (Asthapana Vasti)
Water-based enema that includes:
-
Herbal decoctions (Kashaya)
-
Honey
-
Rock salt
-
Medicated oils
Usually administered in the morning on an empty stomach.
Benefits of Niruha Vasti for PCOS
-
Removes the Avarana of Vata caused by Kapha and Meda
-
Clears Ama (toxins) and improves metabolism
-
Regulates bowel movements and reduces bloating
-
Supports healthy weight reduction
-
Normalises Apana Vata, essential for menstruation and reproductive health
Common decoctions used
-
Dashamoola Kashaya
-
Triphala Kashaya
-
Erandamoola Kashaya
b. Anuvasana Vasti
Oil-based enema, smaller in volume, and retained for a longer time.
Given after food or after Niruha Vasti.
Benefits of Anuvasana Vasti in PCOS
-
Nourishes and strengthens reproductive tissues
-
Balances Apana Vata for healthy menstruation and ovulation
-
Enhances ovarian function
-
Relieves painful periods, dryness, fatigue, and mental stress
Common oils used
-
Ksheerabala Taila
-
Sahacharadi Taila
-
Mahanarayana Taila
-
Bala Taila
c. Yapana Vasti
A special type combining the benefits of Niruha and Anuvasana Vasti.
Benefits of Yapana Vasti in PCOS
-
Strengthens reproductive tissues
-
Improves egg quality
-
Regularises menstrual cycles
-
Supports long-term hormonal balance
-
Ideal for chronic PCOS, infertility, and recurrent miscarriages
d. Uttara Vasti
A specialised enema is administered through the vaginal (Yoni) or urethral route under strict medical supervision.
Benefits of Uttara Vasti in PCOS
-
Acts directly on the uterus and ovaries
-
Effective for endometrial thickening, ovarian cysts, and hormonal imbalance
-
Improves fertility and supports ovulation
-
Helps reduce cyst formation
-
Should be performed only in the post-menstrual phase
Common medicines used
-
Phala Ghrita
-
Shatavari Ghrita
-
Triphaladi Tailam
-
Narayana Tailam
e. Matra Vasti
A mild form of Anuvasana Vasti using 25–60 ml of medicated oil.
It can be administered daily for longer periods.
Benefits of Matra Vasti in PCOS
-
Balances Apana Vata
-
Improves pelvic circulation
-
Provides long-term nourishment without risk of depletion
General Guidelines for Vasti
-
Should be done after Deepana–Pachana (improving digestive fire).
-
Not recommended during pregnancy, active infection, severe weakness, or extreme fatigue.
-
Must be performed under the guidance of a qualified Ayurvedic physician.
5. ناسيا
Nasya is an Ayurvedic therapy where medicated oils or herbal extracts are administered through the nostrils. In PCOS, Nasya helps by acting on the hypothalamic–pituitary axis, the centre that controls hormone secretion, menstrual cycles, ovulation, stress response, and thyroid function.
Benefits of Nasya in PCOS
-
Balances reproductive hormones by regulating the neuroendocrine system
-
Reduces stress and anxiety, which are major triggers for hormonal imbalance
-
Supports thyroid health, improving metabolism and menstrual regularity
-
Enhances sleep quality, helping stabilise hormonal rhythms
-
Improves mood and emotional balance
-
Boosts pituitary and ovarian communication, aiding healthy ovulation
-
Clears toxins in the head–neck region, supporting overall wellbeing
Common Nasya Oils Used in PCOS
-
Anu Taila
-
Ksheerabala Taila
External Ayurvedic Treatments for PCOS
1. Udwartanam

Udwartanam is a classical ayurvedic dry or wet powder massage, where herbal powders(choornas) are rubbed against the hair direction on the body using specific strokes. Normally, in our hospital, Rooksha Udwartanam(dry massage) is followed.
Herbal powders such as Kolakulathadi Choorna and Triphala Choorna are used. The therapy lasts for 30–45 minutes, and is usually followed by Swedana (steam therapy) for enhanced detoxification.
Benefits of Udwartanam in PCOS
-
Reduces Kapha and Meda (excess fat and metabolic toxins)
-
Improves circulation and supports natural detoxification
-
Helps correct hormonal imbalance
-
Promotes regular menstrual cycles
-
Enhances skin texture
2. Abhyanga
Abhyanga is a classical Ayurvedic therapy where warm, medicated herbal oils are rhythmically massaged across the entire body using long, synchronised strokes. Medicated oils such as Dhanwantharam Tailam, Pinda Tailam, etc., are selected based on the patient’s body type and clinical condition.
A typical Abhyanga session lasts 45–60 minutes and is often followed by Swedana (herbal steam therapy) to improve absorption of the oils and promote deeper detoxification.
Benefits of Abhyanga in PCOS
-
Nourishes the body and balances Vata
-
Reduces stress and calms the nervous system (essential for hormonal balance)
-
Improves blood circulation and lymphatic drainage
-
Supports regular menstrual cycles
-
Enhances metabolic function and reduces fatigue
-
Promotes healthy, glowing skin
3. سويدانا
Swedana is a therapeutic herbal steam bath performed after an oil massage. The warm steam induces sweat, opens bodily channels (srotas), and encourages the elimination of toxins that accumulate due to metabolic imbalance.
Herbal decoction made of Dashamoola is used to generate the medicated steam. Sessions typically last 10–20 minutes, supervised by trained therapists to ensure safe heat exposure and optimal benefits.
Benefits of Swedana in PCOS
-
Promotes natural detoxification and reduces Ama (toxins)
-
Boosts blood circulation and supports healthy metabolism
-
Helps reduce Kapha accumulation and body heaviness
-
Relieves muscle tension and improves flexibility
-
Enhances the therapeutic effects of Abhyanga and other treatments
4. شيرودهارا
Shirodhara is an Ayurvedic therapeutic procedure in which warm herbal oil is continuously poured over the forehead (Ajna Marma). This induces profound relaxation and helps regulate the mind–body connection. In our hospital, Ksheerabala oil is commonly used for this therapy.
A typical Shirodhara session lasts 30–45 minutes and is performed in a calm, meditative environment to maximise its soothing effects.
Benefits of Shirodhara in PCOS
-
Reduces stress, anxiety, and emotional imbalance
-
Lowers cortisol (stress hormone), aiding hormonal regulation
-
Supports regular ovulation and menstrual cycles
-
Improves sleep quality and mental clarity
-
Enhances overall reproductive health
Role of Yoga and Pranayama in PCOS
Yoga and pranayama provide a gentle, sustainable, and holistic way to manage PCOS symptoms. They help improve hormonal balance, reduce stress, enhance circulation, and support reproductive health.
Yoga Asanas for PCOS
1. SuptaBaddha Konasana (Reclining bound angle pose)
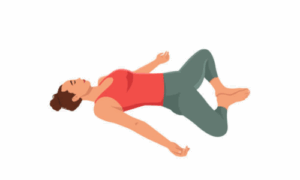
فوائد
- It opens up the pelvic region.
- Stimulates the ovary.
- Reduces menstrual pain.
- It improves circulation.
- It relaxes the lower back.
This pose is ideal for women with hormonal imbalances or menstrual irregularities.
2. Bhujangasana(Cobra pose)
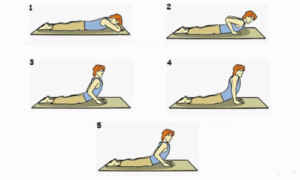
فوائد
- Stimulates ovarian function.
- It improves circulation to the pelvic organs.
3. Setu Bandhasana (Bridge pose)
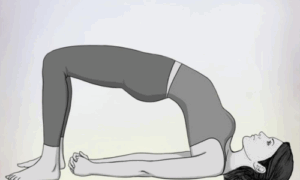
فوائد
- It balances thyroid and hormone levels.
- It strengthens pelvic floor muscles.
- It opens up the chest and shoulders.
- It also relieves menstrual discomfort and mild backaches.
4. Dhanurasana (Bow pose)

فوائد
- It stimulates abdominal organs and improves digestion.
- It helps relieve menstrual discomfort.
- It enhances the breathing capacity.
5. Malasana (Garland pose)
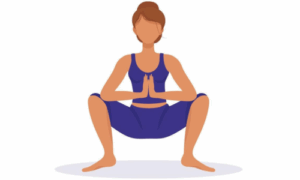
فوائد
- It strengthens the lower body and supports pelvic health.
- It improves digestion and reproductive health.
- It enhances posture.
6. Paschimottanasana (Seated forward bend)
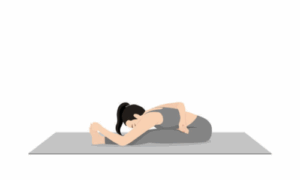
- It stretches the entire back body.
- It stimulates abdominal organs.
- It improves flexibility.
- It is beneficial for menstrual discomfort.
- It calms the nervous system.
- It regulates the endocrine system.
7. Ustrasana (Camel pose)
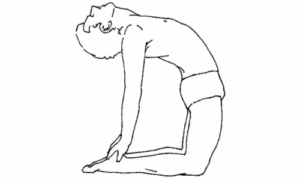
فوائد
- It opens up the chest and abdomen.
- It reduces stress and improves reproductive function.
- It stretches and strengthens the back and shoulders.
- It energises the body and mind.
PRANAYAMA FOR PCOS
Pranayama helps regulate the prana(vital energy) and influences the neuroendocrine system, which is critical in PCOS.
Effective Pranayama techniques:
1. Nadi Shodhana (Alternate nostril breathing)
- It balances both brain hemispheres and hormones.
- It is calming and reduces anxiety and anger.
2. Bhramari (Bee breathing)

- It soothes the nervous system.
- It improves pituitary functions(which control ovarian hormones).
3. Kapalabhati (Skull shining breath)
- It stimulates the ovaries and pancreas.
- It reduces abdominal fat.
- It increases metabolic rate.
4. Ujjayi (Victorious breath)

- It reduces mental restlessness.
- It increases focus.
5. Sheetali/Sheetkari (Cooling breath)
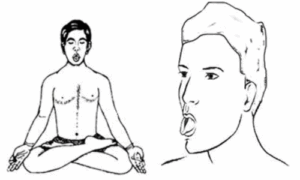
- It cools the mind and body.
- It helps during heat or mood disturbances.
Physiotherapy for PCOS
Physiotherapy addresses the metabolic, musculoskeletal, and hormonal imbalances associated with PCOS. Regular, guided physiotherapy improves insulin sensitivity, reduces abdominal fat, promotes hormonal balance, and enhances reproductive health.
Benefits of Physiotherapy in PCOS
-
Improves Insulin Sensitivity: Exercise enhances glucose uptake and stabilises blood sugar levels, reducing insulin resistance.
-
Supports Weight Loss and Fat Reduction: Metabolic training helps reduce PCOS-related abdominal fat and promotes healthy weight management.
-
Regulates Hormones: Consistent exercise normalises estrogen, progesterone, and androgen levels.
-
Enhances Fertility: Improved pelvic circulation supports ovulation and reproductive function.
-
Reduces Pain: Helps manage pelvic discomfort, lower back pain, and muscle tightness.
-
Improves Mental Health: Exercise reduces depression, anxiety, fatigue, and stress.
Physiotherapy Techniques Used
-
Aerobic Training: Walking, cycling, treadmill workouts, and HIIT
-
Strength Training: Weights, resistance bands, and body-weight exercises
-
Core Strengthening Exercises
-
Pelvic Floor Physiotherapy
-
Stretching and Mobility Training
-
Postural Correction and Ergonomic Guidance
Acupuncture for PCOS
Acupuncture therapy stimulates specific points on the body to regulate the hormonal, metabolic, and nervous systems. It improves reproductive health, insulin sensitivity, and emotional well-being.
How Acupuncture Helps in PCOS
-
Regulates Menstrual Cycles: Improves communication between the brain and ovaries, promoting regular ovulation.
-
Reduces Excess Androgens: Helps manage acne, hair growth (hirsutism), and hair thinning.
-
Improves Insulin Sensitivity: Reduces insulin resistance and prevents weight gain.
-
Enhances Fertility: Increases blood flow to the uterus and ovaries, improving egg quality.
-
Reduces Stress & Anxiety: Balances cortisol levels and promotes restful sleep.
-
Balances Hormonal Levels: Normalises LH, FSH, estrogen, and progesterone balance.
Types of Acupuncture Used
-
Body Acupuncture: Targets hormonal points in the abdomen, back, and legs
-
Scalp Acupuncture: Stimulates neuro-endocrine balance
-
Auricular (Ear) Acupuncture: Controls cravings, appetite, and stress
-
Electroacupuncture: Improves ovarian response and follicle development
-
Reflexology: Reduces stress and supports organ function
General Diet and Lifestyle Suggestions
Along with Ayurveda, physiotherapy, acupuncture, and yoga interventions, diet and lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing symptoms, improving insulin sensitivity, and supporting hormonal balance.
Foods to Avoid or Reduce
To manage PCOS effectively, it is important to limit foods that spike blood sugar and worsen insulin resistance.
-
Refined carbohydrates: White rice, maida (refined flour), biscuits, breads, cakes, pasta, and white sugar
-
Packaged and sugary drinks: Soft drinks, packaged juices, and excess caffeine
-
Sweets and desserts: Chocolates, candies, ice creams, pastries, and bakery items
Reducing these foods helps control weight, regulate blood sugar, and prevent excess androgen production.
Recommended Food Items
Include foods that are light, easy to digest, and support metabolic balance.
-
Hot kanji (porridge) – easy on the digestive system
-
Steamed foods: Idiyappam, puttu, and chapati
-
Boiled vegetables – retain nutrients while being easy to digest
These foods help maintain steady blood sugar levels and support hormonal health.
General Lifestyle Recommendations
Lifestyle habits play a key role in managing PCOS effectively.
-
Avoid strenuous or extreme activities that may stress the body.
-
Hydration: Drink 2.5–3 litres of water daily
-
Sleep: Maintain 7–8 hours of quality sleep
-
Exercise: Regular walking, yoga, and strength training help regulate metabolism and hormonal balance
-
Meal timings: Maintain consistent meal schedules to stabilise blood sugar
At Maurya Ayurveda, our root-focused PCOS treatment enhances hormonal balance, improves metabolic function, and supports long-term well-being.
DISCLAIMER: The information provided in this article is intended solely for educational purposes. Treatment decisions should be made exclusively by a well-qualified Ayurvedic physician. Self-medication is strongly discouraged.
Maurya Ayurveda Hospital, opposite to Sabine Hospital, Pezhakkapilly P.O, Muvattupuzha, Ernakulam; PIN:686673, Contact no:9947183000
Email: info@mauryaayurveda.com
مركز ماوريا أيورفيدا لتقويم العظام وإعادة التأهيل العصبي (مستشفى الأيورفيدا)