BRAIN INJURY CARE THROUGH THE AYURVEDIC THERAPIES!
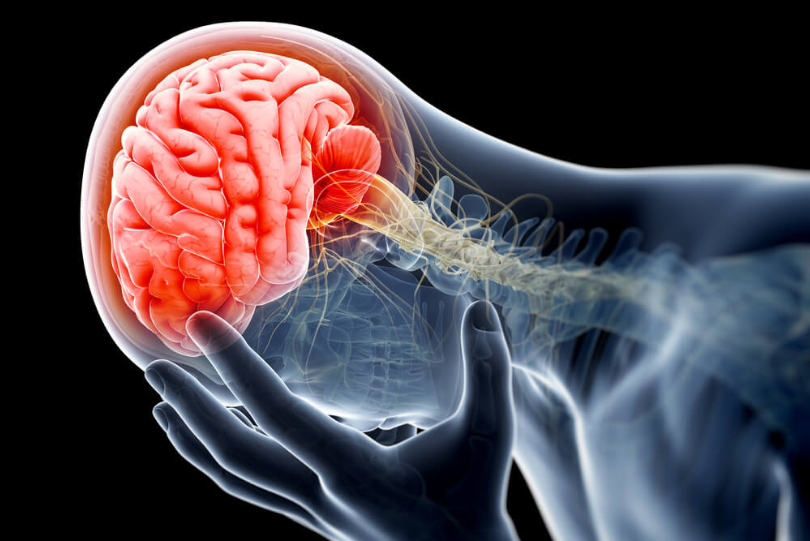
A brain injury is any damage to the brain that impairs its normal function, caused by an external physical force, lack of oxygen, disease, or other internal factors. Brain injuries can affect physical, cognitive, emotional, and sensory functions and their severity ranges from mild(temporary disruptions) to severe(long term disability or death).
In Ayurveda, brain injuries are correlated to “Shiro Abhighatha”(head trauma) or Majja dhathu vikara(disorders of the nervous system). The brain and nervous system are governed by Vata dosha, with disturbances in Vata being a primary concern in traumatic brain injuries. Additionally, the imbalance in pitta (due to inflammation) and kapha (due to edema or obstruction) may also be involved.
TYPES OF BRAIN INJURIES:
Brain injuries can be classified into two main categories:
- Traumatic brain injuries.
- Acquired brain injuries
A)Traumatic Brain injuries:
- These are caused by an external force impacting the head or skull. Common subtypes include:
I)Concussion:
- A mild TBI results in a temporary disruption of brain function.
- Symptoms: Confusion, headache, dizziness, and memory issues.
II)Contusion:
- A localized bruise on the brain, often resulting from direct impact.
- It may require surgery if bleeding or swelling occurs.
III)Diffuse Axonal injury(DAI):
- Widespread damage to brain nerve fibers is caused by rapid acceleration.
- Eg: Car accidents.
- Symptoms: Loss of consciousness, severe cognitive and motor impairments.
IV)Penetrating injury:
- It occurs when an object breaches the skull and damages the brain tissues. Eg: gunshot wounds.
- Severity depends on the extent and location of the injury.
V)Coup-contrecoup injuries:
- It occurs when the brain impacts opposite sides of the skull due to a forceful blow.
- Common in vehicle accidents and falls.
VI)Second impact syndrome:
- It is a rare condition in which a second TBI occurs before the first one has fully healed.
- It can result in severe swelling and fatal outcomes.
2.Acquired Brain injury(ABI):
These are non-traumatic injuries caused by internal factors. Subtypes include:
I)Hypoxic or anoxic brain injury:
- Caused by reduced (hypoxia) or complete lack of oxygen(anoxia) supply to the brain.
- Common causes: Cardiac arrest, drowning, suffocation, or poisoning.
II)Stroke:
- Interruption of blood flow to the brain due to blockage(ischemic stroke) or rupture(hemorrhagic stroke).
- It can lead to localized or widespread brain damage.
III)Brain tumors:
- Growth of abnormal cells within the brain, leads to pressure and damage to surrounding tissue.
IV)Infections:
- Eg: Meningitis(inflammation of the protective membranes) or encephalitis (inflammation of brain tissue)caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi.
V)Toxic/Metabolic Injury:
- Caused by exposure to harmful substances(eg: carbon monoxide poisoning)or metabolic disorders(eg: diabetes leading to hypoglycemia).
VI)Degenerative Diseases:
- Conditions like Alzheimer’s, parkinsonism, or Huntington’s can gradually damage brain cells.
CLINICAL SYMPTOMS OF BRAIN INJURY:
The clinical symptoms of a brain injury vary depending on its severity, type, and the area of the brain affected. Symptoms can be categorized into physical, cognitive, emotional, and sensory domains. Below is a comprehensive breakdown.
General Symptoms of Brain Injury:
1. Physical Symptoms:
- Headache: Persistent or severe headaches are common after a brain injury.
- Nausea or vomiting: Often occurs, especially in more severe cases.
- Dizziness and balance issues: Difficulty in maintaining balance, feeling unsteady.
- Fatigue: A common symptom, even after minor injuries.
- Seizures: Can occur due to abnormal electrical activity in the brain.
- Sensory issues: Blurred vision, ringing in the ears(tinnitus)altered sense of taste or smell.
2. Cognitive symptoms:
- Confusion and disorientation:
- Difficulty in understanding surroundings or the passage of time.
- Memory problems: Short-term or long-term memory loss.
I)Mild Traumatic Brain Injury(Concussion):
Symptoms of mild brain injury (Eg: a concussion)often resolve within days or weeks but may occasionally persist longer.
Physical Symptoms:
- Headache.
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Fatigue or drowsiness.
- Dizziness or loss of balance.
- Sensitivity to light and noise.
Cognitive Symptoms:
- Confusion or disorientation.
- Difficulty concentrating or remembering.
- Mental fog.
- Delayed reaction times.
Emotional symptoms:
- Mood swings(irritability, sadness, anxiety).
- Feeling depressed or emotionally unstable.
Sensory symptoms:
- Blurred or double vision.
- Tinnitus(ringing in the ears).
- Altered taste or smell.
II)Moderate to severe traumatic brain injury:
More severe injuries may lead to long-lasting or permanent impairments.
Symptoms may manifest immediately or worsen over time.
- Persistent headache or worsening headache.
- Convulsions or seizures.
- Dilation of one or both pupils.
- Clear fluid(cerebrospinal fluid) leaking from the nose or ears.
- Weakness or numbness in extremities.
- Difficulty in walking or coordinating movements.
Cognitive Symptoms
- Profound confusion or disorientation.
- Severe memory deficits.
- Inability to concentrate or process information.
- Problems with speech(slurring, inability to find words).
Behavioral and Emotional Symptoms:
- Agitation, combativeness, or unusual behavior.
- Severe mood swings.
- Loss of interest in activities or emotional flatness.
Coma or vegetative state:
In extreme cases, severe brain injuries can lead to a lack of responsiveness with minimal awareness of surroundings.
III)Symptoms by specific brain regions:
The symptoms of a brain injury often reflect the specific area of the brain that is affected:
A)Frontal lobe(Thinking, behavior, movement):
- Impaired judgment or decision-making.
- Changes in personality or social behavior.
- Loss of motor control or weakness on one side of the body.
B)Temporal lobe(Memory, Language):
- Difficulty understanding or speaking language(aphasia).
- Short-term memory loss.
- Seizures(common in temporal injuries).
C)Parietal lobe(Sensation, spatial awareness):
- Impaired ability to recognize objects, places, or people.
- Loss of sensation or inability to perceive touch.
- Difficulty with spatial orientation.
D)Occipital lobe(Vision):
- Vision loss or blindness.
- Difficulty recognizing shapes, colors, or objects.
E)Cerebellum(Balance, coordination):
- Poor coordination.
- Difficulty walking or maintaining balance.
- Tremors or involuntary movements.
F)Brainstem(Vital Functions):
- Loss of consciousness.
- Impaired breathing or heart rate.
- Difficulty swallowing or speaking.
4)Secondary Symptoms: Secondary effects of brain injuries may develop hours to days later:
- Cerebral Edema: Swelling of the brain, leading to increased intracranial pressure(ICP).
- Hematomas: Blood clot formation, compressing brain tissue.
- Hydrocephalus: Accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
- Infections: Meningitis or brain abscesses in cases of penetrating injuries.
5) Long-term symptoms and complications:
- Post-concussion Syndrome: Persistent symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, and cognitive issues.
- Chronic Traumatic encephalopathy(CTE): Progressive neurodegenerative disease caused by repetitive brain injuries.
- Epilepsy: Increased risk of seizures post-injury.
- Psychological disorders: Depression, anxiety, or post-traumatic stress disorder(PTSD).
DIAGNOSIS OF BRAIN INJURY:
The diagnosis of brain injury typically involves identifying damage to the brain that may result from trauma, lack of oxygen, infection, or other causes. The process usually includes clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and functional assessments.
1. Medical History and patient assessment:
- The diagnostic procedure begins with understanding the circumstances surrounding the injury, including:
- Mechanism of injury: Was it a fall, road accident, sports injury, assault, or another trauma?!
- Symptoms: Headache, dizziness, nausea, confusion, loss of consciousness or seizures.
- Time since injury: Helps determine whether the injury is acute, subacute, or chronic.
- Medical History: Includes prior head injuries, neurological conditions, medications, or alcohol/drug use.
2. Physical And neurological Examination:
A detailed physical and neurological examination assesses the following:
a)Level of consciousness: Using the Glasgow coma scale(GCS) to evaluate eye, verbal and motor responses(scores range from 3-15).
- Mild brain injury: GCS: 13-15.
- Moderate brain injury: GCS: 9-12.
- Severe brain injury: GCS: <8.
b)Cranial nerve function:
- Test for vision pupil response, facial symmetry, and other cranial nerve functions.
- Motor and sensory function: Strength, coordination, reflexes, and sensation of limbs.
- Cognitive and behavioral evaluation: Memory, attention span, speech, and mood changes.
3. Imaging Studies:
Imaging is crucial for identifying structural brain injuries:
a)CT Scan(computed tomography):
- First-line imaging in acute brain injury due to its speed and accuracy.
- Detects fractures, bleeding(hematomas), brain swelling, contusions and herniation.
b)MRI(Magnetic Resonance Imaging):
- More sensitive for soft tissue injuries.
- Defects diffuse axonal injury(DAI), small hemorrhages, ischemia, or non-acute injuries.
c)Angiography:
- If vascular injury(Eg: aneurysm, dissection)is suspected, CT or MR angiography can assess blood vessels.
4)Advanced Diagnostic Tools:
- Intracranial pressure(ICP) Monitoring: For severe injuries, a probe measures pressure inside the skull.
- Electroencephalogram(EEG): Detects abnormal activity, such as seizures.
- Diffusion Tensor Imaging(DTI): It’s a type of MRI, used to visualize white matter and detect diffuse axonal injuries.
- Functional MRI(fMRI): Assess brain activity in specific regions.
5)Laboratory tests:
- Lab tests may be used to assess:
- Blood biomarkers for brain injury: Eg: S100B, GFAP.
- Coagulation profiles to rule out bleeding disorders.
- Blood glucose and oxygen levels, as they affect brain recovery.
6. Neuropsychological testing:
For milder injuries or persistent symptoms, neuropsychological testing evaluates:
- Memory.
- Attention and concentration.
- Problem-solving abilities.
- Emotional and psychological changes.
7. Observation and follow-up:
- For mild injuries, patients may undergo observation to watch for worsening symptoms:
- Monitoring for repeated vomiting, worsening headache, confusion, or seizures.
- Follow-up imaging for evaluation after a few days if symptoms persist or worsen.
Types of Brain Injuries Diagnosed:
- Traumatic Brain Injury(TBI): Includes concussions, contusions, and penetrating injuries.
- Diffuse Axonal Injuries(DAI): Common in high-speed trauma.
- Hematomas: Epidural, subdural, or intracerebral bleeding.
- Hypoxic ischemic injury: Caused by lack of oxygen.
- Cerebral edema: Brain swelling.
TREATMENT OF BRAIN INJURY IN MAURYA AYURVEDA HOSPITAL:
Our unique approach merges Ayurveda, physiotherapy, and acupuncture to achieve the best possible outcomes for brain injury rehabilitation. Here are the treatments we provide:
EXTERNAL TREATMENT IN AYURVEDA:
THALAM:

Thalam is a specialized ayurvedic treatment in which medicated herbal paste or oil is applied to the head, particularly the crown area. Normally Thalam is applied prior to every treatment, which prevents ENT-related conditions like headache, running nose, cold, fever, etc.
Normally Kachuradi along with Ksheerabala is used for this condition.
Advantages of Thalam in Brain injury management:
- It enhances neurological functions.
- It improves blood circulation.
- It aids in mental clarity and relaxation.
- It also supports neuroplasticity and recovery.
PODIKIZHI:

It is called ChoornaPindaSweda. Podi Kizhi is an Ayurvedic therapy technique that involves massage with cotton bags(pottali) loaded with medicinal powder, which is warmed and used. KOLAKULATHADI CHOORNAM is used for the same purpose.
The advantages of Podi kizhi are:
- It helps reduce pain and swelling.
- It improves mobility and motor function.
- It increases the flow of blood.
- It reduces inflammation.
- It strengthens the muscles and joints.
- It reduces muscle spasms and stiffness.
- It promotes the nervous system healing.
UDWARTHANAM:

A unique form of Ayurvedic massage known as “Powder massage,” or “Udwarthanam,” uses herbal powders to knead the body more vigorously in the direction opposite to the hair follicles. This is typically accomplished with either Kolakulathadi or Kolakulathadi with Triphala Choornam.
Advantages of the Udwarthanam
- It stimulates the nervous system.
- It enhances metabolic activity
- It makes the blood flow more rapid.
- It reduces swelling.
- It improves coordination and mobility.
- It aids in detoxification.
NADI SWEDAM:

It’s a kind of “sweating therapy” or sudation treatment that involves applying therapeutic steam to specific body parts via a hose or tube. It’s considered one of the greatest treatments in Ayurveda for conditions including neurological diseases, stiff joints, cramping muscles, and other conditions caused by an imbalance between the Vata and Kapha doshas.
Advantages of Nadi Swedam:
- It improves blood flow.
- It reduces pain.
- It aids in the reduction of muscle stiffness and spasticity.
- Promotes detoxification.
- Improves mobility.
DHARA

Dhara is a common Ayurvedic medicinal technique that involves continuously pouring medicated liquids into certain body locations, such as the forehead, targeted areas, or the entire body.
Normally we perform DHANYAMLA DHARA (using DHANYAMLA-a fermented liquid ) and KASHAYA DHARA (DASHAMOOLA KASHYAM used).
Advantages of DHARA
- Promotes nervous system healing.
- Relaxes muscle spasticity.
- Reduces inflammation.
- Improves sleep patterns.
- Relieves stress and anxiety.
- Neuroprotective in effect.
- Muscle relaxation.
SHIRO DHARA:

Shirodhara is the process of applying heated medicinal oil, herbal mixtures, or other therapeutic liquids to the forehead on a regular, rhythmic basis. It is commonly known that this therapy can calm the nervous system.
In this case, KSHEERABALA TAILA is frequently employed for the same purpose.
TAKRADHARA:

The technique known as Takradhara involves pouring medicinal buttermilk rhythmically over the forehead (Shirodhara) or the full body (Sarvanga dhara). Shirodhara is beneficial for treating neurological disorders and stress.
- Curd (yogurt) is churned with water to remove the butter component, creating buttermilk.
- Adding herbal decoctions of Musta (Cyperus rotundus) or Amalaki (Indian gooseberry) improves its therapeutic qualities.
- Usually, it lasts between 30 and 60 minutes.
Benefits of Shirodhara and Takradhara.
- It aids in calming and relaxing the nervous system.
- It improves mental clarity and focus.
- It enhances blood circulation.
- It reduces headaches and migraine.
- It provides better sleep.
NASYAM:

Nasyam involves the administration of medicinal oils or powders through the nose. A light face massage is given in the beginning. It is followed by applying steam to the face and neck to open channels and enhance absorption. The medicated oil or powder is administered to one of the nostrils followed by the other, and the patient is asked to inhale gently to ensure the medicines reach nasal cavities, again a face massage is given. The patient is advised to lie in the supine position for about 5-10 minutes to allow the medicine to penetrate deeply. Also, the patient can spit out secretions formed in the mouth.
Nasyam types:
- Marsha Nasya: In Marsha Nasyam higher doses of medicinal powder, or oil are used like 2-10 drops. Usually, Ksheerabala (101) is used for this.
- Pratimarsha Nasya: A daily preventive kind of nasya therapy, Pramimarsha nasya is the mildest kind of nasya(normally 2 drops). Usually, Anu Taila is used for Pratimarsha Nasyam.
Advantages of Nasya
- It enhances blood circulation and promotes detoxification.
- It alleviates symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, and nasal congestion.
- It enhances sensory and motor skills.
- It improves mental clarity and focus.
- Nervous system rejuvenation.
- Reduces inflammation.
- Calms the nervous system.
THALAPOTHICHIL:
Also known as Shiro Lepa, this treatment involves applying medicinal herbs to a patient’s scalp to treat a variety of neurological and mental conditions. In this case, a medicinal plant paste is first applied to the patient, covering the entire scalp with banana leaves. Next, a Thalam is administered using a medicinal oil such as Ksheerabala, Chandanadi, or Valiya Chandanadi.
Amala (Indian gooseberry, Phyllanthus emblica) and Musta (nut grass, Cyperus rotundus) Rasnadi Choornam, Curd, Usheera (Ramacham, Vetiveria zizanioides), and Kachuram (Kachuram, Curcuma zedoaria) are used to make the medicinal paste.
The advantages of Thalapothichil in Brain Injury are:
- Enhanced brain function.
- Improved blood circulation.
- Reduces stress and anxiety.
- Detoxification.
- Supports healing.
SHIRO VASTHI AND SHIRO PICHU:
SHIRO VASTI:

Vasthi means a holding or container, while Shiras signifies head. Warm medicinal oils are applied to the scalp and left there for a predetermined time (about 30 to 60 minutes) in a specially made cap or container. The edges are sealed with a black gram flour paste. Ksheerabala Taila is often used after being warmed. To promote relaxation and improved absorption, the head is gently massaged after the procedure.
SHIRO PICHU:

Shiro Pichu is applying a heated medicinal oil-soaked cotton towel or pad to the top of the head. Ksheerabala Taila is used for the same procedure. It usually takes about twenty minutes.
Advantages of Shiro vasthi and shiro pichu:
- It promotes mental calmness.
- It helps reduce stress and anxiety.
- It helps reduce headaches and stress.
- It improves the standard of sleep.
- Restoring mental clarity.
PHYSIOTHERAPY AND ITS ADVANTAGES IN BRAIN INJURY:
To meet the unique needs of patients, for healing from brain injuries, physiotherapists use a variety of treatments. These methods promote neuroplasticity, increase strength, and restore mobility. They are given below:
1)Range of Motion(ROM) exercises:
- Passive Range of Motion Exercise: The physiotherapist moves the patient limbs passively when the patient cannot move independently.
- Active Range of Motion Exercises: The patient performs movements on their own, often targeting strength and coordination in weakened or paralyzed muscles.
Advantages of ROM in Brain injury:
- It helps in maintaining joint health.
- It prevents contractures and stiffness.
- It improves circulation.
2)Neurodevelopmental Techniques(NDT):
- Focus on retraining the brain to perform normal movement patterns.
- Includes facilitation of desired movements and inhibition of abnormal reflexes or patterns.
Advantages of NDT in Brain injury:
- It promotes neuroplasticity.
- It encourages normal motor control.
3)Gait Training:

It helps patients relearn walking using techniques like:
- Parallel bar: It provides support while retraining basic walking mechanics.
- Treadmill training: It can include body weight support for safety.
Advantages of Gait training in Brain injury:
- It improves mobility and balance.
- It enhances lower limb strength and coordination.
4)Strengthening Exercises:
- Isometric exercises.
- Isotonic exercises.
- Progressive Resistance Training(PRT).
- Functional Training.
- Core strengthening.
- Body weight exercises.
- Dynamic strengthening.
A few pieces of equipment normally used in strengthening exercises are:
- Resistance bands, weights or dumbbells, therapy balls, leg presses, etc.
Advantages of Strengthening exercises in Brain injury:
- It restores muscle strength.
- It presents muscle atrophy.
- It improves functional abilities.
- It enhances endurance and stamina.
- It supports neuroplasticity.
5)Balance and Coordination Exercises:
I)Balance Exercises:
a)Static Balance Exercises:
- Standing with feet together.
- Single leg stance.
- Tandem stance.
Benefits:
- It improves stability.
- Strengthening core and lower body muscles.
b)Dynamic Balance Exercises:
- Weight shifting.
- Heel-to-toe walking.
- Stepping over Obstacles.
Benefits:
- It enhances walking stability.
- It improves adaptability to uneven surfaces.
c)Proprioceptive Training:
- Balance boards.
- Foam pads.
- Eye-closed Balance.
II)Coordination Exercises:
- Hand-eye coordination.
- Cross-body movements.
- Stepping patterns.
III)Core stability exercises:
- Bridging.
- Plank variations.
- Seated balance exercises.
IV)Vestibular rehabilitation:
- Head movements.
- Gaze stabilization exercises.
- Walking with head turns.
V)Dual-Task training:
- Walking while counting backward.
- Balance while holding objects.
Advantages of Balance and Coordination exercises:
- It improves postural control.
- It reduces the risk of falling.
- It enhances functional mobility.
- It aids in motor coordination.
- It increases confidence.
- It improves neuroplasticity.
6)Functional Electrical Stimulation(FES):
It’s a therapeutic technique that is used to restore or improve motor function in individuals with neurological injuries, including brain injuries. It works by delivering small electrical impulses to specific muscles or muscle groups, causing them to contract. This helps them to improve motor control, prevent muscle atrophy, and promote neuroplasticity.
Advantages of FES in brain injury:
- It restores voluntary movement.
- It improves muscle strength and prevents atrophy.
- It reduces muscle spasticity.
- It enhances neuroplasticity.
- It promotes functional recovery.
- It improves circulation.
- It reduces secondary complications.
Uses of FES in brain injury Rehabilitation:
- Upper limb rehabilitation.
- Swallowing therapy.
- Gait training.
- Postural control.
7)Vestibular Rehabilitation Therapy(VRT):
Components of Vestibular Rehabilitation Therapy(VRT)
- Habituation exercises
- Gaze Stabilization Exercises.
- Balance Training.
- Strength and endurance training.
- Dual-Task training.
- Functional Training.
Benefits of Vestibular Rehabilitation for Brain injuries:
- Improved balance and stability.
- Reduce dizziness and vertigo.
- Enhanced visual stability.
- Restored mobility and independence.
- Enhanced cognitive function.
- Minimizing the likelihood of falls and associated injuries.
8)Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy(CIMT):
- CIMT is an effective physiotherapy intervention for improving upper limb function following brain injury, traumatic brain injury, stroke, or cerebral palsy.
Common exercises in CIMT:
- Picking up small objects(Eg: coins or blocks).
- Functional tasks like buttoning, pouring water, or brushing teeth.
- Reaching and grasping tasks with progressive difficulty.
Benefits of VRT in Brain injury:
- It improves coordination, strength, and functional use of affected limbs.
- It enhances the ability to perform ADL (Activities of Daily Living).
- It aids in neuroplasticity.
- It improves self-efficacy and reduces dependence on caregivers.
9. Use of Assistive devices like:
- Braces, orthotics, or mobility aids like walkers for enhanced functionality.
10. Using TENS and ULTRASOUND:


- TENS: It involves the application of low-voltage electrical currents through skin to stimulate nerves.
- Ultrasound: It uses high frequency sound waves to stimulate tissues and promote healing.
Benefits of TENS:
- Pain management.
- Spasticity reduction.
- Improving sensory feedback.
- Neuromuscular re-education.
Benefits of Ultrasound:
- Tissue healing.
- Reduction of inflammation.
- Pain relief.
ROLE OF ACUPUNCTURE IN BRAIN INJURIES:
Acupuncture, a component of traditional Chinese medicine, has gained attention as a complementary therapy in managing brain injuries. Its role primarily revolves around promoting neuroprotection, neuro regeneration, and functional recovery.
Key techniques of Acupuncture:
1)Body Acupuncture:
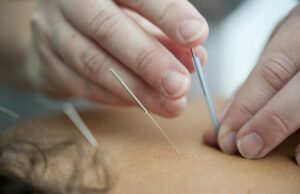
- It involves inserting needles at meridian points associated with the brain and nervous system.
Point based on symptoms:
1. Motor impairments:
- DU20,GB20,L11,ST36,DU14.
2. Cognitive Dysfunction:
- DU20,PC6,EX-HN1,SP6.
3. Spasticity or paralysis:
- L14,LI11,ST40,SP6.
4. Speech Impairments:
- DU20,DU16,PC6,CV23(Lianquan).
5. Emotional Disorders:
- LR3,SP6,DU20,HT7(Shenmen).
2) Electroacupuncture(EA):
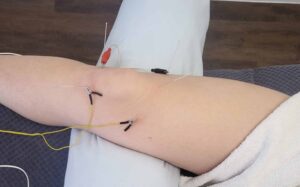
- Combines traditional acupuncture with low-frequency electrical stimulation.
- Often used for spasticity, or motor recovery by stimulating neuroplasticity and nerve regeneration.
- A session usually lasts about 10-20 minutes.
Benefits of Acupuncture in brain injury:
- It enhances motor recovery By improving muscle strength, coordination, and mobility in patients with paralysis or spasticity.
- It aids in better focus, memory, and problem-solving abilities due to cerebral blood flow and regulation of neurotransmitters.
- It helps to relax hypertonic muscles and aids patients attain voluntary movement, by reducing muscular spasticity and stiffness.
- It aids in pain relief from neck strain, chronic headaches, or post-injury discomforts.
- It also helps in reducing anxiety, depression, and irritability which are common after injury.
- It enhances neuroplasticity.
- It prevents secondary complications by balancing autonomic nervous system functions and improving sleep, appetite, and immunity.
Techniques of Yoga and Pranyama in Brain Injury:
Yoga and Pranayama are effective complementary therapies for brain injury rehabilitation.
Key techniques of Yoga for brain injury:
1.Gentle Asanas(Physical Postures):
- Tadasana(Mountain pose): Improves posture, balance, and stability.
- Vrikshasana(Tree pose): Enhances focus and body awareness.
- Balasana(child pose): Relaxes the mind and releases stress.
- Bhujangasana(cobra pose): Stimulates the spine and improves circulation to the brain.
- Setu Bandhasana(Bridge pose): Promotes blood flow to the brain and strengthens core muscles.
Benefits:
- It improves muscle coordination and joint mobility.
- It aids in blood and oxygen flow to the brain.
- It reduces muscle stiffness and spasticity.
2.Yoga Nidra(Yogic sleep):
- It’s a guided relaxation technique that brings the mind into a deeply relaxed yet aware state.
Benefits:
- It improves focus and mental clarity.
- It reduces anxiety, depression, and emotional instability which appear common after brain injuries.
3. Restorative Yoga:
- It focuses on deep relaxation through supported poses and mindful breathing.
- Techniques like Savasana(corpse pose) with guided relaxation.
- The pose is supported with bolsters and cushions.
- Benefits: It reduces stress, promotes brain healing, and calms the nervous system.
Approaches in Pranayama for brain injury:
Pranayama involves controlled breathing techniques that regulate the autonomic nervous system and enhance the oxygen supply to the brain.
1.Nadi Shodhana(Alternate nostril breathing):
Technique:
- Inhale, through the left nostril, exhale through the right, and alternate.
- Practice slowly and rhythmically.
Benefits:
- It reduces stress and anxiety, stabilizing the nervous system
- It enhances focus and cognitive function.
2.Bhramari Pranayam(Humming bee breath):
Technique:
- Inhale deeply and exhale while producing a humming sound.
- Focus on the vibration created in the head region.
Benefits:
- It calms the mind and improves memory.
- It stimulates the parasympathetic nervous system, reducing inflammation.
- It helps manage emotional instability.
- Anuloma-Viloma(controlled alternate breathing):
- Technique: Inhale deeply, retain breath, and exhale slowly.
- Retention of breath(Kumbhaka), may be involved in advanced practice.
Benefits:
- It increases the oxygenation of brain tissues.
- It improves emotional resilience and mental clarity.
- It enhances lung function, which is normally impaired in bedridden patients.
4.Kapalabhati(Cleansing Breath):
Technique:
- Forceful exhalation followed by passive inhalation.
- To be practiced gently for individuals with brain injury.
Benefits:
- It improves circulation and detoxification.
- It stimulates brain activity and clears mental fog.
- It enhances focus and alertness.
5.Ujjayi Pranayama(Victorious breath):
Technique:
- Inhale deeply through the nose while slightly contracting the throat to create a whispering sound.
Benefits:
- It improves oxygen delivery to the brain.
- It reduces stress and induces relaxation.
DIET RECOMMENDATIONS IN OUR HOSPITAL:
General Suggestion:
- Stay away from physically demanding activities.
- Drink two to three liters of water.
| FOOD ITEMS TO BE TAKEN: | FOOD ITEMS TO BE AVOIDED: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
DISCLAIMER: The information provided in this article is intended solely for educational purposes. Treatment decisions should be made exclusively by a well-qualified Ayurvedic physician. Self-medication is strongly discouraged.
Maurya Ayurveda Hospital, opposite to Sabine Hospital, Pezhakkapilly P.O,Muvattupuzha,Ernakulam;PIN:686673,Contact no:9947183000
Email: info@mauryaayurveda.com
Maurya Ayurveda Ortho & Neuro Rehabilitation Centre ( Ayurveda Hospital )