AYURVEDA FOR CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME(CTS): HEAL YOUR HANDS NATURALLY
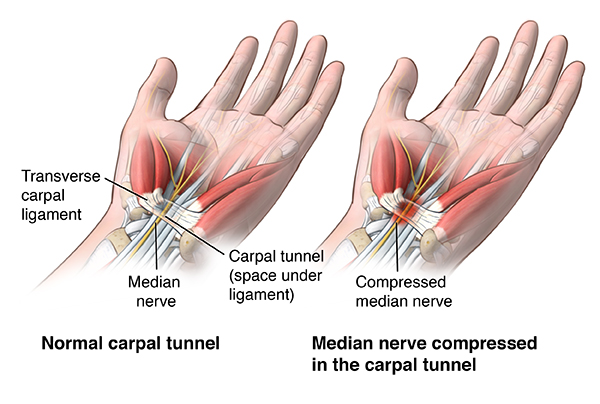
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a common nerve compression disorder that affects the hand and forearm. It occurs when the median nerve, one of the major nerves of the hand, is compressed as it passes through the carpal tunnel in the wrist. This compression can lead to numbness, tingling, pain, and weakness in the hand.
Carpal Tunnel Anatomy
The carpal tunnel is a narrow, rigid passageway in the wrist, approximately one inch wide.
It is formed by:
- Carpal bones – forming the floor and sides of the tunnel
- Transverse carpal ligament – forming the roof
- Nine flexor tendons also pass through the tunnel to bend fingers and the thumb
Role of the Median Nerve
- Originates from nerve roots in the neck
- Travels down the arm and forearm to the wrist
- Passes through the carpal tunnel
- Branches into smaller nerves in the palm
- Provides sensation to the thumb, index, middle, and half of the ring finger
- Controls key thumb muscles for gripping and fine motor movements
Causes and Risk Factors of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome occurs when:
- The tunnel becomes narrower, OR
- The synovium (the tissue surrounding the flexor tendons) swells
- This increases pressure on the median nerve, reducing blood flow and causing symptoms.
Key causes and risk factors include:
Anatomical Changes
- A naturally narrow carpal tunnel, sometimes inherited
- Women generally have smaller carpal tunnels than men
- Bone or joint changes from arthritis, trauma, or fractures
Swelling and Inflammation
- Repetitive hand movements or prolonged wrist extension/flexion
- Rheumatoid arthritis or other joint inflammatory conditions
- Hormonal or metabolic changes (pregnancy, menopause, thyroid disorders)
Other Contributing Factors
- Diabetes or fluctuations in blood sugar
- Wrist injuries (strain, sprain, dislocation, fracture)
- Obesity
Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Symptoms often worsen over time and may be more noticeable at night.
Common signs include:
- Numbness in the thumb, index, and middle fingers
- Tingling or “pins and needles” sensation
- Hand or wrist pain
- Weak grip strength
- Difficulty holding objects
- Burning or tingling in the fingers, especially the thumb, index, and middle fingers
- Swollen feeling in the fingers
Ayurvedic View of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS)
- In Ayurveda, CTS is linked to Vata imbalance in the Manibandha Sandhi (wrist joint).
- It corresponds to “Manibandha Sandhi Sthita Snayugata Vata, where aggravated Vata affects the Snayu (tendons, ligaments, and nerves) of the wrist.
Why CTS is Considered a Vata Disorder
- Vata governs: nerve impulses, movement, sensory perception, and flexibility
- Aggravating factors: repetitive strain, overuse of the wrist, cold exposure, dryness
Pathophysiological Effects
- Constricted carpal tunnel space
- Dryness of tendons and soft tissues
- Stiffness and inflammation
- Impaired median nerve function
These Vata-driven changes result in pain, tingling, numbness, and restricted wrist movement, which are characteristic symptoms of CTS.
Diagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Physical Examination
During the physical exam, the doctor will ask about your symptoms, overall health, and medical history. They will then examine your hand and wrist and may perform several standard tests used to diagnose Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, including:
-
Tinel’s Sign
The doctor lightly taps or presses along the median nerve on the palm side of your wrist.
- Tingling or “electric shock” sensations in the fingers suggest nerve irritation.
-
Wrist Flexion Test (Phalen’s Test)
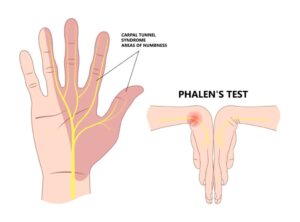
You bend and hold your wrists in a flexed position.
- Numbness or tingling indicates possible median nerve compression.
-
Sensory Testing
A specialised tool is used to touch your fingertips while your eyes are closed lightly.
- This checks for reduced sensation caused by nerve dysfunction.
-
Thumb Strength Testing
The doctor evaluates the muscles at the base of your thumb (thenar muscles).
- Weakness may indicate more advanced CTS.
-
Inspection for Muscle Atrophy
In severe or long-standing CTS, the thumb muscles may appear visibly smaller due to prolonged nerve compression.
Diagnostic Tests for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Electrodiagnostic Testing
These tests evaluate how well the median nerve sends signals.
-
Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS)
Measures the speed and strength of nerve signals in the hand and arm.
Helps determine the severity of nerve compression.
2. Electromyogram (EMG)
Measures electrical activity in muscles.
- Identifies nerve damage, muscle damage, or conditions such as neuropathy.
Electrodiagnostic testing can also determine:
- Whether the nerve is compressed in multiple locations
- Whether other nerves are affected
- Whether another underlying condition is contributing to symptoms
Imaging Tests for CTS
-
Ultrasound
Uses sound waves to create images of soft tissues.
- Helps identify swelling or compression of the median nerve.
-
X-Rays
Although X-rays cannot diagnose CTS directly, they help rule out:
- Arthritis
- Fractures
- Ligament injuries
- Other causes of wrist pain
-
MRI
Provides detailed images of soft tissues.
- Useful for detecting abnormal structures, tumours, scarring, or other issues that may affect the median nerve.
Treatments for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) in Maurya Ayurveda
Ayurveda in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS)
1. Podi Kizhi (Choorna Pinda Swedana)
Podi Kizhi is a traditional Ayurvedic Swedana (sudation) therapy involving heated herbal powders tied in a cloth pouch (Kizhi).
Procedure
- Heat herbal powders, mainly Kolakulathadi Choornam, and tie in a muslin cloth to form a Kizhi.
- Warm the Kizhi and apply it over the wrist, hand, and forearm.
Benefits for CTS
- Reduces inflammation and swelling
- Relieves stiffness and pain
- Improves blood circulation around the median nerve
- Helps reduce numbness and tingling
2. Avagaham (Medicated Immersion Therapy)
Procedure
- The palm and wrist are immersed in warm herbal decoctions.
Benefits
- Reduces stiffness
- Soothes nerve compression
- Improves blood flow
3. Lepam (Herbal Paste Application)
Lepam is a traditional Ayurvedic external therapy using a warm herbal paste.
Procedure
- A freshly prepared medicated paste is applied over the affected wrist and allowed to stay until semi-dry.
Benefits
- Quick relief from pain and swelling
- Reduces local inflammation
- Helps reduce pressure on the median nerve
4. Dhara
Dhara is an Ayurvedic therapy in which a continuous stream of warm, medicated liquid is poured over the wrist.
Procedure
- Warm herbal decoction, fermented liquid, buttermilk, or medicated oil is poured steadily from a height over the wrist.
Benefits
- Calms irritated nerves
- Reduces pain and burning sensation
- Relaxes muscles and tendons around the carpal tunnel
Dhanyamla Dhara
Dhanyamla Dhara uses fermented herbal liquid (Dhanyamla) for stronger anti-inflammatory effects.
Procedure
- Warm Dhanyamla is poured continuously over the wrist and forearm in a rhythmic motion.
Benefits
- Reduces swelling and stiffness
- Improves wrist movement and nerve function
5. Upanaham
Upanaham is an Ayurvedic poultice therapy using medicinal paste and leaves to relieve wrist pain and nerve irritation.
Procedure
- Apply medicinal paste over the affected wrist.
- Cover with medicated leaves and bandage for a specific duration.
Benefits
- Reduces pain and swelling around the median nerve
- Nourishes deep tissues, improving circulation and healing
- Calms Vata imbalance, relieving stiffness, tingling, and nerve irritation
6. Abhyangam (Medicated Oil Massage)
Abhyangam is a traditional Ayurvedic massage using warm medicated oils.
Procedure
- The wrist, palm, and forearm are massaged using rhythmic strokes.
Benefits
- Improves blood flow
- Relaxes muscles and nerves
- Enhances joint mobility
7. Pichu (Oil-Soaked Cotton Therapy)
Pichu is an Ayurvedic therapy where cotton pads soaked in warm medicinal oil are applied to the wrist to relieve pain and improve nerve function.
Procedure
- Apply thick cotton soaked in warm medicated oil over the affected wrist.
- Replace the oil regularly to maintain warmth and therapeutic effect.
Benefits
- Deeply nourishes tissues
- Reduces chronic pain
- Supports nerve function recovery
8. Nasya (Nasyam)
Nasya is a classical Ayurvedic therapy in which medicated oil is administered through the nostrils. It is especially beneficial for disorders of the nervous system, head, neck, shoulders, and upper limbs, making it useful in the management of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome.
Procedure
-
The patient lies comfortably on their back with the head slightly tilted.
-
A gentle oil massage is given to the face, neck, and shoulders.
-
Mild steam (fomentation) is applied to the face and neck.
-
2–4 drops of warm medicated oil are instilled into each nostril.
-
The patient is instructed to inhale gently.
-
Any oil that reaches the throat is spat out.
-
Cold exposure, wind, dust, and daytime sleep are avoided for a few hours after the procedure.
Common Oils Used for Nasya in CTS
-
Anu Taila
-
Ksheerabala Taila
Benefits of Nasya in CTS
-
Reduces pain, numbness, and tingling in the hands
-
Relieves nerve compression
-
Improves blood circulation to the upper limbs
-
Strengthens and nourishes nerves
-
Balances aggravated Vata Dosha
-
Helps prevent progression of CTS
9. Greeva Basti
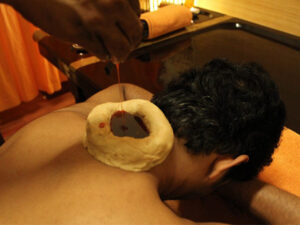
Greeva Basti is an external Ayurvedic therapy where warm medicated oil is retained over the neck (cervical region) for a fixed time.
CTS symptoms often worsen due to cervical nerve compression, poor circulation, and muscle tightness. Greeva Basti helps address these root causes by nourishing nerves, relaxing muscles, and improving blood flow.
Procedure
-
The patient lies face down.
-
The dough ring is placed on the neck.
-
Warm medicated oil is poured into the ring.
-
Oil is retained for 20–30 minutes.
-
Followed by a gentle neck massage
Benefits
-
Reduces cervical nerve compression
-
Relieves neck and shoulder stiffness
-
Improves circulation to arms and hands
-
Reduces numbness, tingling, and pain
-
Balances Vata Dosha
-
Improves nerve function and mobility
10. Agnikarma (Thermal Cautery Therapy)

Agnikarma is an Ayurvedic therapy using controlled heat to relieve wrist pain and nerve compression.
Procedure
Controlled application of heat using a metal rod at specific points.
Benefits
- Immediate pain relief
- Reduces nerve compression
- Improves circulation
- Effective for severe or chronic CTS
Physiotherapy in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Through targeted exercises, manual therapy, and therapeutic modalities, physiotherapy helps reduce symptoms, improve mobility, and enhance hand function.
1. Wrist Rotations
Procedure
- Extend the arm forward.
- Rotate the wrist slowly in a clockwise direction.
- Rotate the wrist in an anti-clockwise direction.
Benefits
- Improves blood circulation
- Loosens stiff wrist joints
- Reduces morning or activity-related stiffness
2. Finger Stretch
Procedure
- Spread all fingers as wide as possible.
- Hold for a few seconds, then relax.
Benefits
- Stretches finger tendons
- Reduces the tightness of flexor tendons
- Decreases finger numbness or heaviness
3. Wrist Flexor Stretch
Procedure
- Extend the arm with palm facing upward.
- Gently pull the fingers backwards until stretch is felt in the forearm.
Benefits
- Reduces tight wrist flexor muscles
- Relieves pressure on the median nerve
- Improves wrist flexibility
4. Wrist Extensor Stretch
Procedure
- Extend the arm with palm facing downward.
- Gently push the fingers downward using the opposite hand.
Benefits
- Relieves tension in wrist extensor muscles
- Balances wrist muscle groups
- Reduces compression inside the carpal tunnel
5. Prayer Stretch (Namaste Stretch)
Procedure
- Join palms together in front of the chest.
- Lower hands slowly while keeping palms pressed together.
Benefits
- Deeply stretches wrist flexor muscles
- Increases space in the carpal tunnel
- Helps decrease nerve compression
6. Median Nerve Glide
Procedure
- Start with a closed fist.
- Open the hand and straighten fingers.
- Extend the wrist backwards.
- Turn the palm outward.
- Tilt the head gently to the opposite side.
Benefits
- Mobilises the median nerve
- Reduces nerve entrapment
- Decreases tingling, burning, and radiating pain
7. Tendon Glides
Procedure
Move the fingers through these positions:
- Straight hand
- Hook fist
- Full fist
- Table-top position
- Straight fist
Benefits
- Improves tendon movement inside the carpal tunnel
- Prevents adhesions
- Enhances finger mobility
8. Grip Strengthening (Soft Ball Squeeze)
Procedure
- Hold a soft ball in the palm.
- Gently squeeze and pause.
- Release slowly.
Benefits
- Improves grip strength
- Supports wrist stability
- Helps in daily functional activities
9. Wrist Isometrics
Procedure
- Apply gentle pressure against the hand in different directions (flexion, extension, radial deviation) without moving the wrist.
Benefits
- Strengthens wrist safely
- Enhances wrist stability
- Prevents further irritation of the median nerve
10. Rubber Band Finger Extension
Procedure
- Place a rubber band around the fingers.
- Open fingers outward slowly against resistance.
Benefits
- Strengthens finger extensor muscles
- Balances hand muscle groups
- Reduces strain from repetitive finger flexion
Therapeutic Modalities
11. Ultrasound Therapy
Procedure
- Pulsed ultrasound is applied over the carpal tunnel region.
Benefits
- Reduces inflammation
- Promotes tissue healing
12. Cold Pack Application
Procedure
- Apply a cold pack over the wrist for 10–15 minutes.
Benefits
- Reduces swelling
- Decreases burning sensation
- Helps during acute flare-ups
Manual Therapy
13. Carpal Bone Mobilisation
Procedure
- Therapist performs gentle mobilisation of the carpal bones.
Benefits
- Increases joint space
- Improves carpal alignment
- Reduces pressure on the median nerve.
14. Soft Tissue Release
Procedure
- Therapist releases tight forearm flexors and thenar muscles.
Benefits
- Relieves muscle tension
- Reduces strain on the carpal tunnel
- Improves hand function
Night Care
15. Night Splinting
Procedure
- Wear a neutral-position wrist brace during sleep.
Benefits
- Prevents excessive wrist bending
- Reduces nighttime numbness
Offers the best results among conservative CTS treatments.
Yoga for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Yoga is a gentle and effective way to relieve symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS).
Regular practice helps by:
- Improving flexibility in the wrists and forearms
- Reducing inflammation through controlled movement and better circulation
- Strengthening the hand, wrist, shoulder, and upper-back muscles
- Improving posture, which is a major cause of CTS
- Relaxing tension in the neck and upper back, reducing pressure on the median nerve
Best Yoga Poses for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
1. Wrist Stretch (Prayer Pose)
Bring your palms together at chest height.
Slowly lower your hands toward your waist until you feel a gentle stretch inside your wrists.
Benefits
Opens the carpal tunnel and reduces pressure on the median nerve.
2. Reverse Prayer Stretch
Place your hands behind your back with the backs of the palms touching.
Lift slightly to stretch the top of the wrists.
Benefits
Releases tight forearm muscles.
3. Cat–Cow (Spine–Neck Release)
Begin on your hands and knees, but stay on fists or forearms to avoid wrist pressure.
Slowly alternate between arching and rounding your back.
Benefits
Reduces tension in the shoulders and neck—common contributors to CTS.
4. Thread the Needle Pose
From a tabletop position, slide one arm under your body and rest your shoulder on the floor.
Benefits
Relieves upper-back tightness that can aggravate wrist pain.
Yoga Poses to Avoid if You Have CTS
Avoid poses that put direct weight on your wrists, including:
- Plank
- Downward-Facing Dog
- Crow Pose
- Handstands
These positions can increase pressure on the median nerve and worsen symptoms.
Acupuncture for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
By stimulating specific acupoints, acupuncture helps relieve pressure on the median nerve, reduce inflammation, and improve blood circulation.
Common Acupuncture Points for CTS
- PC7 – Pericardium point on the wrist
- LI4 – Between the thumb and index finger
- LU9 and LU10 – Thumb-side wrist points
- LI10 and LI11 – Forearm points
- Neck and shoulder points – To improve posture-related nerve compression
Benefits of Acupuncture on CTS
- Reduces pain through natural endorphin release
- Relieves numbness and tingling in fingers
- Eases wrist and forearm tension
- Reduces inflammation around the median nerve
- Improves grip strength and hand mobility
- Promotes tissue healing and natural recovery
Lifestyle Modifications for CTS
-
Ergonomic Adjustments
- Keep wrists neutral; use an ergonomic keyboard and vertical/cushioned mouse
- Adjust chair so elbows stay at 90°; forearms level with desk
- Keep frequently used items within reach
- Phone: avoid bent wrists
- Tools: use larger grips; limit vibrating tools
-
Activity Modification
- Take micro-breaks every 20–30 minutes
- Avoid prolonged gripping, pinching, or twisting
- Alternate hands; reduce long typing, texting, and gaming sessions
-
Anti-Inflammatory Lifestyle
- Include omega-3s, turmeric, ginger, leafy greens, and berries
- Limit sugar, processed foods, and salty snacks
- Maintain a healthy weight
-
Daily Habits
- Avoid sleeping with wrists curled
- Lift with two hands; use ergonomic kitchen tools
- Avoid tight watches or bracelets
-
Stress Management
- Reduce tension with deep breathing, mindfulness, warm showers, and good sleep
-
Reduce Environmental Exposure
- Avoid prolonged cold; wear gloves
- Limit vibration exposure from tools/equipment
-
Smoking Cessation
- Smoking reduces nerve blood flow; quitting improves healing and reduces CTS symptoms
-
Manage Medical Conditions
- Control diabetes, thyroid disorders, arthritis, and fluid retention to reduce carpal tunnel pressure
DISCLAIMER: The information provided in this article is intended solely for educational purposes. Treatment decisions should be made exclusively by a well-qualified Ayurvedic physician. Self-medication is strongly discouraged.
Maurya Ayurveda Hospital, opposite to Sabine Hospital, Pezhakkapilly P.O, Muvattupuzha, Ernakulam; PIN:686673, Contact no:9947183000
Email: info@mauryaayurveda.com
Maurya Ayurveda Ortho & Neuro Rehabilitation Centre ( Ayurveda Hospital )